Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Determine the direction in which a current-carrying wire experiences a force in an external magnetic field
- Calculate the force on a current-carrying wire in an external magnetic field
Force on a Current-Carrying Wire
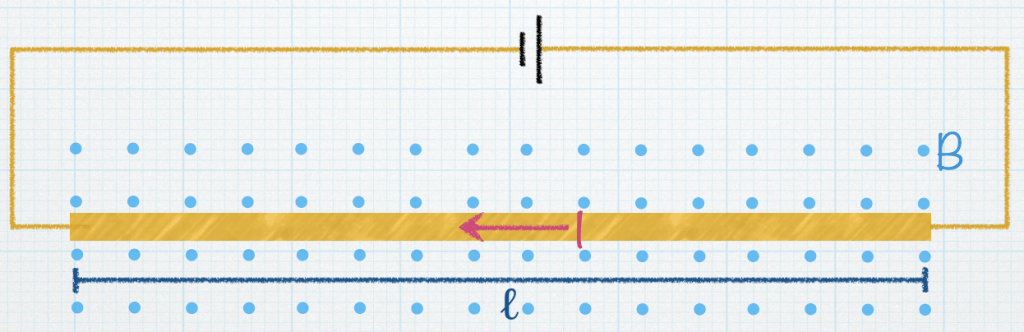
In this circuit, a portion of the wire is immersed in a magnetic field. The length of the wire that is in the field is ℓ. The field has a strength B and points out of the page (as seen from the dots, like a bunch of darts coming right at you, yikes!). Every charge in this wire feels a force from the magnetic field.
| Here is a RHR check: |
|---|
Going back to our definition of conventional current (I = flow of positive charges), what is the direction of the magnetic force on these moving charges?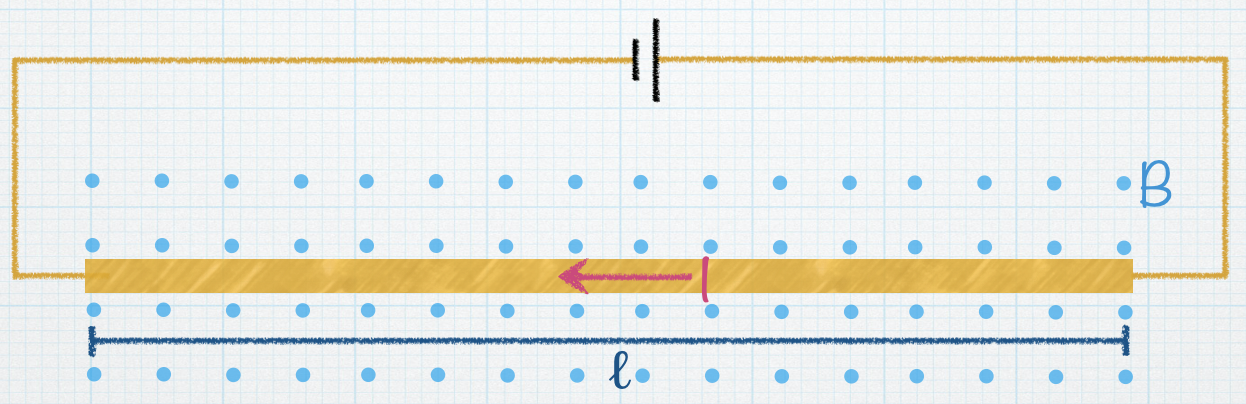 |
| Pause & Predict 10.2.1 |
|---|
| What is the current in the wire if the magnetic force is equal to the gravitational force on the wire? |
| Pause & Predict 10.2.2 |
|---|
| What is the angle between the magnetic dipole moment and the magnetic field? |

Practice!
| Practice 10.2.6 |
|---|
| A 65-cm segment of conducting wire carries a current of 0.35 A. The wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field that has a magnitude of 1.24 T. What is the angle between the wire segment and the magnetic field if the force on the wire is 0.26 N? |
| Practice 10.2.7 |
|---|
| Two long straight wires are parallel to each other and are separated by 78 mm. The current in wire 1 is 3.55 A and the current in wire 2 is 2.75 A. What is the force per unit length between the two wires? |
| Practice 10.2.8 |
|---|
| A circular coil of conducting wire, with a radius of 4.48 cm and 25 turns, is in a 1.67-T magnetic field. When the coil’s dipole moment vector makes an angle of 34° with the magnetic field, a 0.537-N•m torque is exerted on the coil. What is the current in the coil? |

Discuss!
The figure shows a top view of two conducting rails on which a conducting bar can slide. A uniform magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of the figure as shown (into the page, X). A battery is to be connected to the two rails so that when it’s connected, current will flow through the bar and cause a magnetic force to push the bar to the right.

In which orientation, A or B, should the battery be placed in the circuit to result in a magnetic force on the bar that pushes it to the right?