Spherical Mirrors
Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
We already briefly discussed how you see an image formed by a flat mirror. Now we will look at images from curved mirrors. You actually see these all the time, but maybe never thought about how they work.

A concave mirror is a curved mirror whose reflective side is on the inside of the curve, like here:

A convex mirror is a curved mirror whose reflective side is on the outside of the curve, like here:


Practice!
| Practice 16.2.1 |
|---|
| You wish to reflect sunlight from a mirror onto some paper under a pile of wood in order to start a fire. Which would be the best choice for the type of mirror? |
| Practice 16.2.2 |
|---|
The diagram shows three light rays reflected off of a concave mirror. Which ray is NOT correct? |
| Practice 16.2.3 |
|---|
| The image produced by a concave mirror of a real object is… |
| Practice 16.2.4 |
|---|
| The image produced by a concave mirror of a real object is… |
| Practice 16.2.5 |
|---|
| The image produced by a convex mirror of a real object is… |
| Practice 16.2.6 |
|---|
| The image produced by a convex mirror of a real object is… |
| Practice 16.2.7 |
|---|
Take a look at this picture of some NASA scientists working on a mirror for a large telescope.  Based on the appearance of this image, you would conclude which of the following? |
Mirror Equations
The Mirror Equation and Magnification
The mirror equation is:
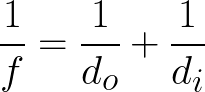
and the magnification is:
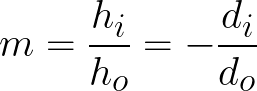
The sign conventions are:
| Converging (Concave) Mirror | Diverging (Convex) Mirror | |
| Real Object | + do | + do |
| Real Image | + di | N/A (convex mirrors cannot form real images) |
| Virtual Image | – di | – di |
| Focal Length | + f | – f |
| Pause & Predict 16.2.1 |
|---|
| Where does the image of the apple form, relative to the mirror? |
| Pause & Predict 16.2.2 |
|---|
| What is the magnification of the image of the apple? |

Practice!
| Practice 16.2.8 |
|---|
| When you hold a spherical concave mirror with a 48.2-cm radius of curvature in front of your face, you see an image of your face that is 61.8 cm in front of the mirror. What is the distance between the mirror and your face? |
| Practice 16.2.9 |
|---|
| When you hold a spherical concave mirror with a 48.2-cm radius of curvature 39.5 cm in front of your face, you see an image of your face that is 61.8 cm in front of the mirror. What is the magnification of this image? |
| Practice 16.2.10 |
|---|
| When you hold a spherical concave mirror with a 48.2-cm radius of curvature 19.4 cm in front of your face, you see an image of your face in the mirror. Where is this image located, with respect to the mirror? |

Discuss!
An automobile rear-view mirror shows an image of a truck at a time when the truck is 3.0 m from the mirror. The focal length of the mirror is -0.58 m.

(a) Find the position of the image of the truck.
(b) Find the magnification of the image.