Coordinate Systems and Components of a Vector

2.2 Coordinate Systems and Components of a Vector
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe vectors in two and three dimensions in terms of their components, using unit vectors along the axes.
- Distinguish between the vector components of a vector and the scalar components of a vector.
- Explain how the magnitude of a vector is defined in terms of the components of a vector.
- Identify the direction angle of a vector in a plane.
- Explain the connection between polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates in a plane.
Trig Review
Before we get into the discussion about vector components, let’s first do a quick review of trigonometry. Test yourself with the following practice problems.

Practice!
| Practice 2.2.1 |
|---|
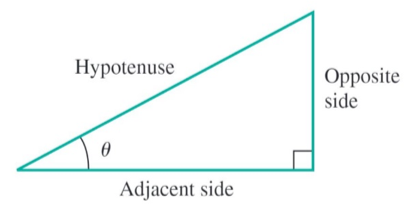 From the figure, how do you define the |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| (e) |
| Practice 2.2.2 |
|---|
 From the figure, how do you define the |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| (e) |
| Practice 2.2.3 |
|---|
 From the figure, how do you define the |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| (e) |
| Practice 2.2.4 |
|---|
 What is the length of the side of the triangle adjacent to θ if θ = 30° and the hypotenuse is 2 units? |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| (e) |
| Practice 2.2.5 |
|---|
 What is the length of the side of the triangle opposite to θ if θ = 30° and the hypotenuse is 2 units? |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| (e) |
| Practice 2.2.6 |
|---|
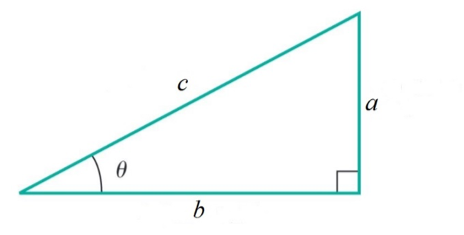 From the triangle in the figure, what is another way to express c? |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| (e) |
Vector Components

Practice!
| Practice 2.2.7 |
|---|
 What is the magnitude of the x-component of vector |
| (a) 14.4 m |
| (b) 10.8 m |
| (c) 13.6 m |
| (d) 18.0 m |
| (e) 12.0 m |
| Practice 2.2.8 |
|---|
 What is the magnitude of the y-component of vector |
| (a) 14.4 m |
| (b) 10.8 m |
| (c) 13.6 m |
| (d) 18.0 m |
| (e) 12.0 m |
Adding Vectors using Vector Components

Practice!
| Practice 2.2.9 |
|---|
 When vector |
| (a) 26.4 m |
| (b) 10.8 m |
| (c) 22.8 m |
| (d) 6.00 m |
| (e) 2.40 m |
| Practice 2.2.10 |
|---|
 When vector |
| (a) 26.4 m |
| (b) 10.8 m |
| (c) 22.8 m |
| (d) 6.00 m |
| (e) 2.40 m |
| Practice 2.2.11 |
|---|
 When vector |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| (e) |
| Practice 2.2.12 |
|---|
 When vector |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| (e) |
| Practice 2.2.13 |
|---|
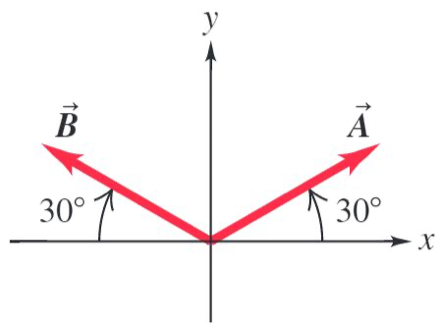 Vectors |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| Practice 2.2.14 |
|---|
 Vectors |
| (a) |
| (b) |
| (c) |
| (d) |
| Practice 2.2.15 |
|---|
 Vectors |
| (a) The resultant |
| (b) The resultant |
| (c) The resultant |
| (d) The resultant |
| (e) The resultant |

Discuss!
Consider how you would answer this question. Then bring this to class for a group discussion.
An ant crawling on a table undergoes three consecutive displacements:
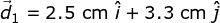
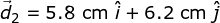
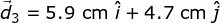
Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement.