Principles of Physics II Course Learning Objectives
and why they matter.
Welcome to our calculus-based physics course on electricity, magnetism, light, and optics. Here are the key things you’ll learn in this course and why they’re important.
Upon completion of this course students will:
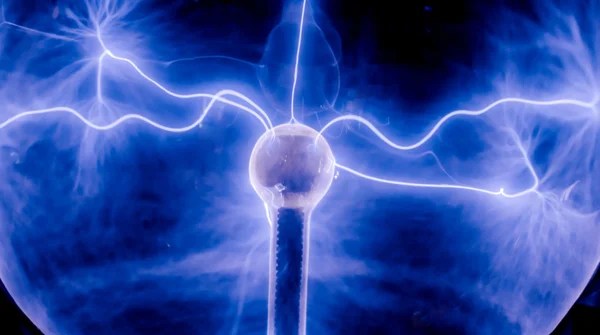
1. Apply fundamental electrostatic principles (Coulomb’s law, electric fields, electric potential) and Gauss’s law to analyze charge distributions and solve related problems.
This will help you grasp how electric charges interact, which is fundamental to understanding all electrical phenomena.
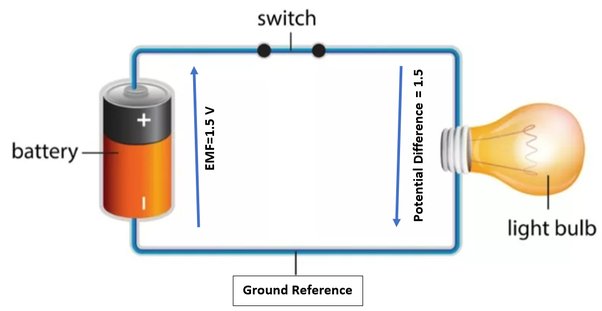
2. Analyze DC circuits using Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s rules, including the behavior of capacitors and RC circuits.
You’ll learn how electricity flows in circuits, which is crucial for understanding all electronic devices.

3. Calculate magnetic forces and fields using the Biot-Savart law and Ampère’s law for various current distributions.
This knowledge is essential for understanding how motors, generators, and many other technologies work.
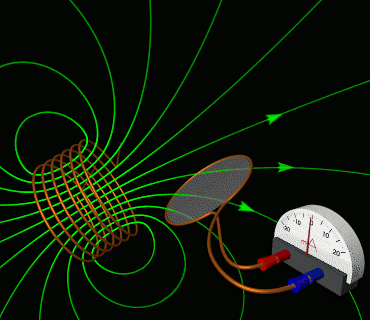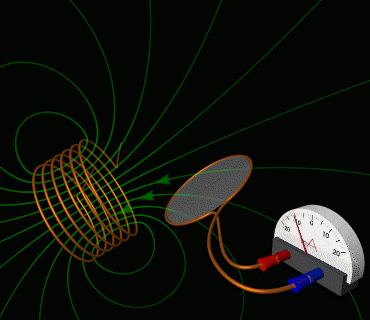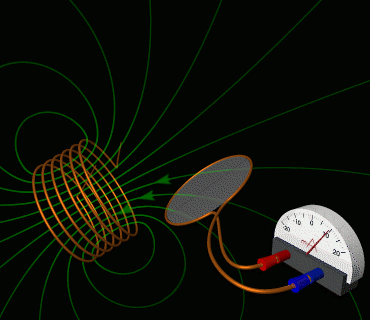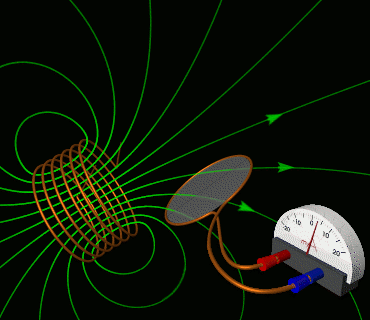
4. Solve electromagnetic induction problems using Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law, including applications of motional EMF and changing magnetic flux.
This skill is key to understanding how we generate and transmit electricity.

5. Analyze AC circuits, including the behavior of inductors, capacitors, and resistors in AC systems, and calculate impedance and power in these circuits.
This knowledge is important for understanding how our power grid works and how many electronic devices operate.

6. Describe the properties of electromagnetic waves, explain their generation and propagation, and demonstrate how Maxwell’s equations lead to the derivation of the speed of light.
This will help you understand how light, radio waves, and other types of radiation behave and are used in technology.
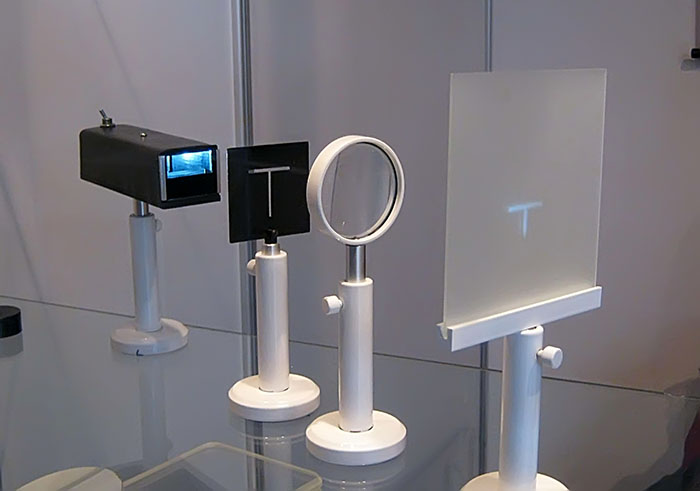

7. Solve geometrical optics problems involving reflection, refraction, mirrors, and lenses using relevant laws and equations.
This knowledge is useful for understanding how lenses work in cameras, glasses, and many other optical devices.
8. Analyze wave optics phenomena, including interference and diffraction, in contexts such as double-slit experiments and diffraction gratings.
This will deepen your understanding of light’s behavior and its applications in technology.

9. Use vector calculus to describe and analyze electromagnetic phenomena across various topics in the course.
This mathematical skill is crucial for describing complex electromagnetic phenomena.

10. Explain the working principles of common electromagnetic devices and relate course concepts to real-world technologies, such as electric power generation and transmission, telecommunications, medical imaging (e.g., MRI), and consumer electronics.
This will help you see how the concepts you’re learning are used in everyday life and cutting-edge technologies.
These objectives are important because they form the foundation of modern physics and engineering. The principles you’ll learn are used in countless technologies, from smartphones to medical imaging devices. Understanding these concepts will give you valuable problem-solving skills and a deeper appreciation of the physical world around you.