Modern Physics Course Learning Objectives
and why they matter.
Welcome to Modern Physics. Here are the key things you’ll learn in this course and why they’re important.
Upon completion of this course students will:

1. Apply Special Relativity: Calculate time dilation, length contraction, and relativistic momentum and energy using the postulates of special relativity and Lorentz transformations.
Why: Understanding special relativity is essential for analyzing high-speed phenomena and lays the foundation for modern technologies like GPS and particle accelerators.
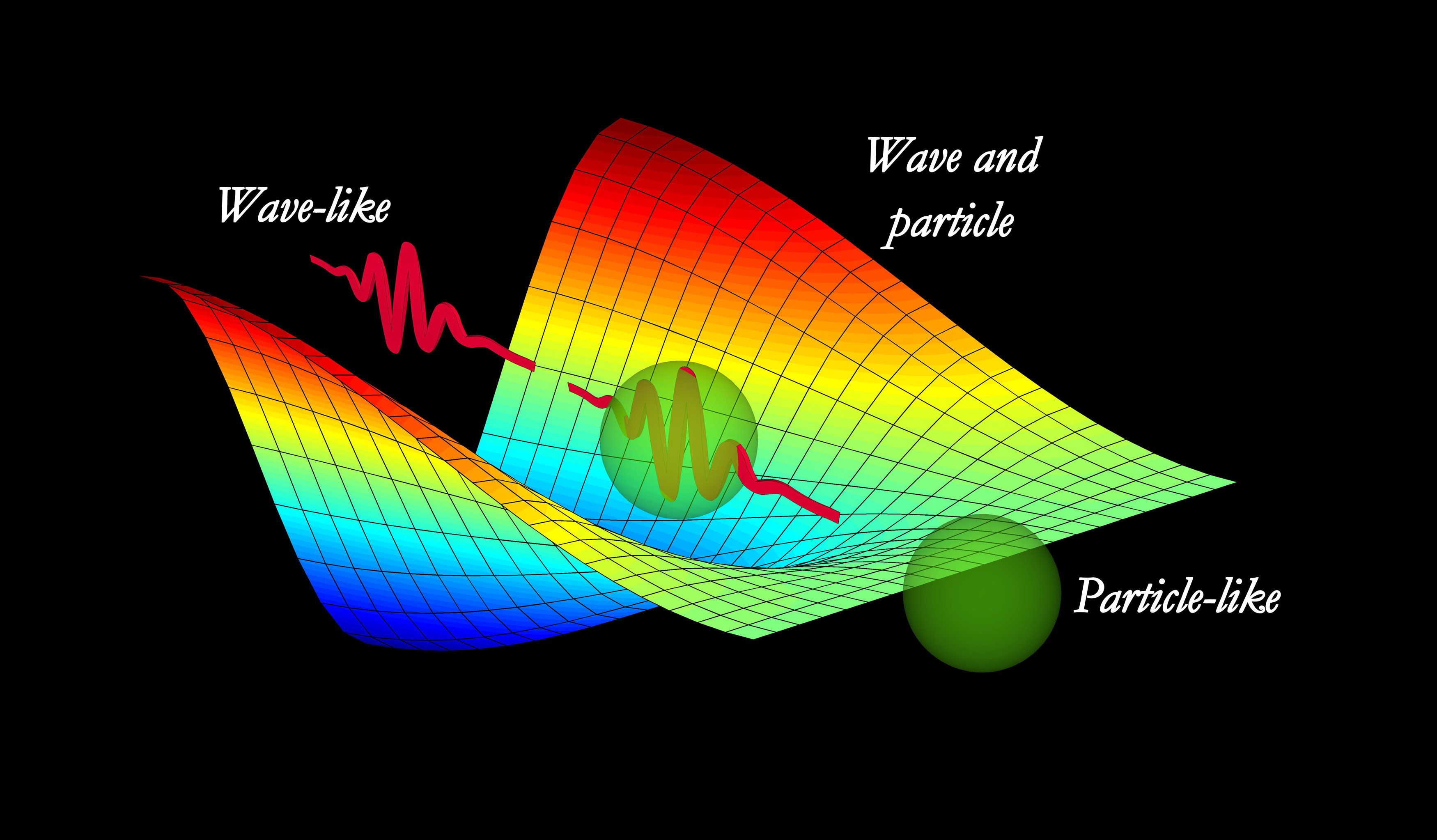
2. Analyze Wave-Particle Duality: Explain the experimental evidence for wave-particle duality and apply concepts such as de Broglie wavelengths and the photoelectric effect to solve problems.
Wave-particle duality is key to understanding quantum mechanics, which underpins technologies such as semiconductors, lasers, and quantum computing.

3. Solve Schrödinger Equation Problems: Solve the Schrödinger equation for simple systems, including particles in a box and quantum harmonic oscillators, to determine wave functions and energy levels.
Why: The Schrödinger equation provides the framework for understanding quantum systems and predicting their behavior, which is critical for advancements in physics and chemistry.

4. Explain Atomic Structure: Describe the quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom, including quantum numbers, orbital shapes, and the Zeeman effect.
Why: A detailed understanding of atomic structure is crucial for explaining chemical bonding, atomic spectra, and the behavior of materials.
5. Interpret Molecular Behavior: Analyze molecular bonding, spectra, and the properties of molecular solids using quantum mechanical principles.
Why: Understanding molecular behavior helps explain the physical and chemical properties of matter, with applications in materials science, chemistry, and biology.

6. Characterize Band Theory and Semiconductors: Use band theory to distinguish between conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, and explain how doping modifies the behavior of semiconductor devices.
Why: Band theory and semiconductors are fundamental to modern electronics, from computers and smartphones to solar cells and LEDs.
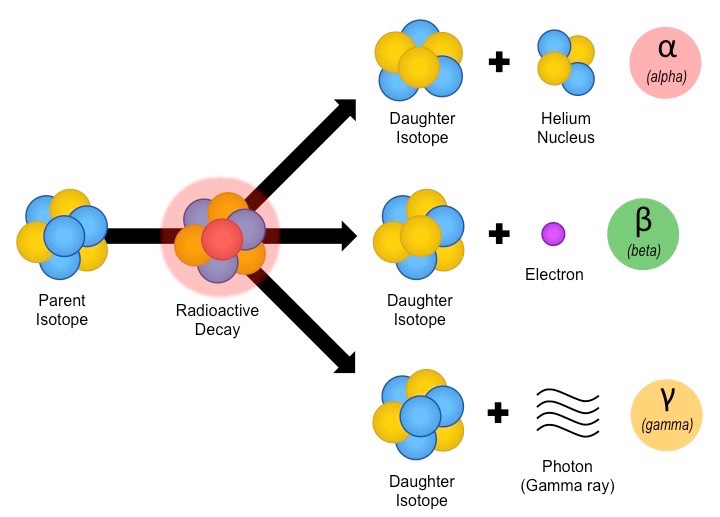
7. Evaluate Nuclear Properties: Calculate nuclear binding energy and interpret the stability of nuclei, as well as describe the processes of radioactive decay and their applications.
Why: Understanding nuclear properties is vital for harnessing nuclear energy, ensuring radiation safety, and advancing medical imaging and treatments.

8. Apply Concepts of Nuclear Reactions: Explain the principles of nuclear fission and fusion, and evaluate their applications in energy production, medical technology, and their biological effects.
Why: Knowledge of nuclear reactions is crucial for addressing global energy challenges, advancing medical therapies, and understanding the processes powering stars.

9. Discuss Particle Physics: Summarize the structure of the Standard Model, apply conservation laws to particle interactions, and explain the role of quarks in forming hadrons.
Why: Particle physics uncovers the fundamental building blocks of the universe and drives cutting-edge research in cosmology, quantum theory, and technology.

10. Connect Quantum Mechanics to Modern Applications: Relate quantum mechanical principles to real-world applications, including lasers, X-rays, and emerging technologies like quantum computing.
Why: Quantum mechanics has revolutionized science and technology, and its applications are transforming industries such as medicine, telecommunications, and computing.
These objectives are important because they form the foundation of modern physics and engineering. The principles you’ll learn are used in countless technologies, from smartphones to medical imaging devices. Understanding these concepts will give you valuable problem-solving skills and a deeper appreciation of the physical world around you.