Relativistic Velocity Transformation

1.6 Relativistic Velocity Transformation
Learning Objectives
- Derive the equations consistent with special relativity for transforming velocities in one inertial frame of reference into another.
- Apply the velocity transformation equations to objects moving at relativistic speeds.
- Examine how the combined velocities predicted by the relativistic transformation equations compare with those expected classically.

Practice!
| Practice 1.6.1 |
|---|
 A rocket travels at speed 0.5c relative to Earth. The rocket shoots a bullet in the forward direction at speed 0.5c relative to the rocket. Is the bullet’s speed relative to Earth less than, greater than, or equal to c? |
| A. less than c |
| B. greater than c |
| C. equal to c |
| Practice 1.6.2 |
|---|
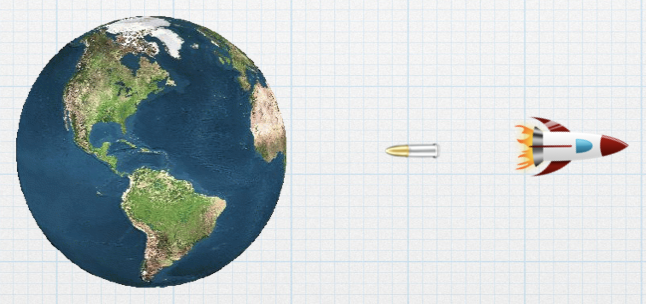 A rocket travels at speed 0.5c relative to Earth. The rocket shoots a second bullet in the backward direction at speed 0.5c relative to the rocket. In Earth’s frame, is the bullet moving right, moving left, or at rest? |
| A. moving right |
| B. moving left |
| C. at rest |
| Practice 1.6.3 |
|---|
 The rocket speeds are shown relative to Earth. Is the speed of A relative to B greater than, less than, or equal to 0.8c? |
| A. greater than 0.8c |
| B. less than 0.8c |
| C. equal to 0.8c |
| Practice 1.6.4 |
|---|
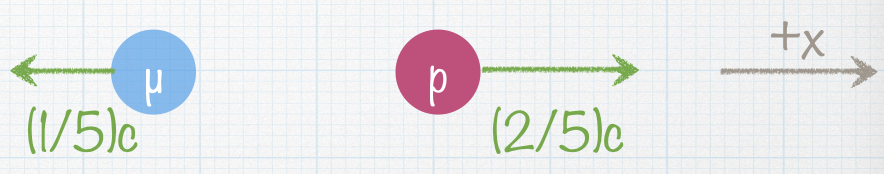 What is the velocity of the muon (µ) in the proton’s (p) frame of reference? |
| A. -(15/23)c |
| B. (5/23)c |
| C. -(15/27)c |
| D. -(5/23)c |
| E. (15/23)c |