Skip to content
Semiconductors and Doping
Learning Objectives
- Describe changes to the energy structure of a semiconductor due to doping
- Distinguish between an n-type and p-type semiconductor
- Describe the Hall effect and explain its significance
- Calculate the charge, drift velocity, and charge carrier number density of a semiconductor using information from a Hall effect experiment
| Practice 11.3.1 |
|---|
| How would you expect the electric conductivity of a semiconductor to vary with increasing temperature? |
| A. It should increase, because more electrons are thermally excited from the valence band into the conduction band. |
| B. It should increase, because more electrons are removed from their parent atoms and added to the valence band. |
| C. It should decrease, because the added thermal energy breaks apart correlated electron pairs. |
| D. It should decrease, because the atoms in the crystal will vibrate more and thus block the flow of electrons. |
| E. It should remain the same, because the band structure does not depend on temperature. |
Check your answer: A. It should increase, because more electrons are thermally excited from the valence band into the conduction band.
Doping Semiconductors
| Practice 11.3.2 |
|---|
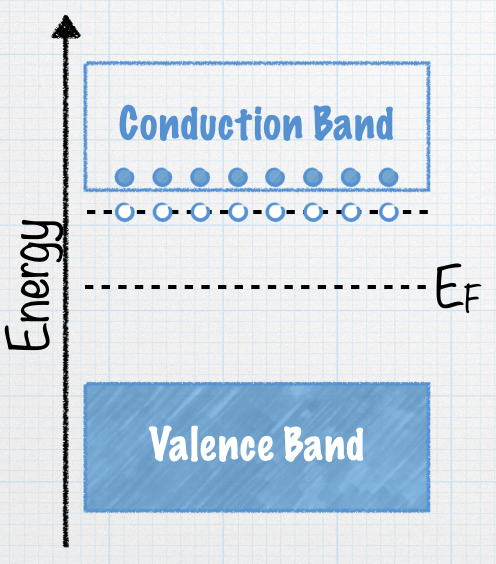
With all those negative charge carriers in the conduction band, we call this an n-type semiconductor. What is the net charge charge on this material? |
| A. positive |
| B. negative |
| C. zero |
Check your answer: C. zero
| Practice 11.3.3 |
|---|
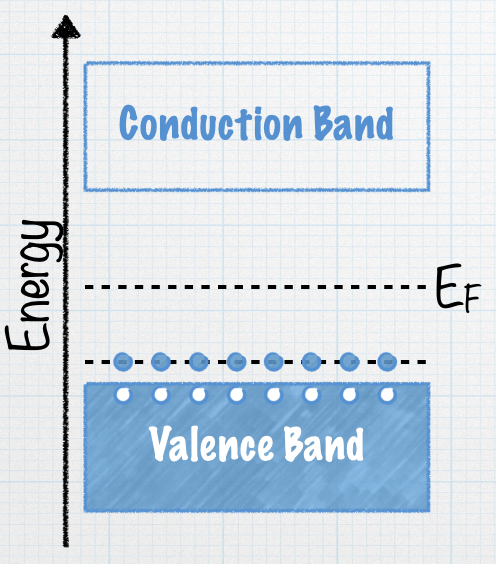
With all those positive charge carriers in the valence band, we call this a p-type semiconductor. What is the net charge charge on this material? |
| A. positive |
| B. negative |
| C. zero |
Check your answer: C. zero
| Practice 11.3.4 |
|---|
| Compared to an intrinsic (pure) semiconductor, what should you expect the conductivity of an n-type doped semiconductor to be? |
| A. lower conductivity |
| B. the same conductivity |
| C. higher conductivity |
Check your answer: C. higher conductivity
| Practice 11.3.5 |
|---|
| Compared to an intrinsic (pure) semiconductor, what should you expect the conductivity of an p-type doped semiconductor to be? |
| A. lower conductivity |
| B. the same conductivity |
| C. higher conductivity |
Check your answer: C. higher conductivity
| Practice 11.3.6 |
|---|
| The difference between donor and acceptor atoms in a doped semiconductor is that |
| A. the donor energy level lies halfway between the valence band and the acceptor level. |
| B. the donor energy level lies near the valence band and the acceptor energy level lies near the conduction band. |
| C. donor energy levels cannot exist unless acceptor energy levels are present. |
| D. the donor energy level lies near the conduction band and the acceptor energy level lies near the valence band. |
| E. the acceptor energy level lies halfway between the conduction band and the donor energy level. |
Check your answer: D. the donor energy level lies near the conduction band and the acceptor energy level lies near the valence band.



