Semiconductor Devices

11.4 Semiconductor Devices
Learning Objectives
- Describe what occurs when n- and p-type materials are joined together using the concept of diffusion and drift current (zero applied voltage)
- Explain the response of a p-n junction to a forward and reverse bias voltage
- Describe the function of a transistor in an electric circuit
- Use the concept of a p-n junction to explain its applications in audio amplifiers and computers

Practice!
| Practice 11.4.1 |
|---|
| An n-type semiconductor and a p-type semiconductor are joined to form a diode (p-n junction). Compared to the total number of electrons in the semiconductors before joining, the number of electrons in the diode is |
| A. fewer |
| B. greater |
| C. the same |
Current in a p-n Junction

Discuss!
Find the current flowing in the circuit.
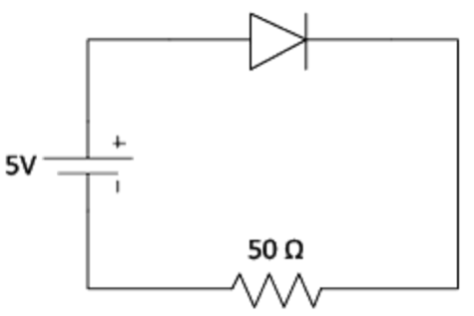
Assume the diode turns on at exactly 0.7 volts of forward bias.