Fission

13.2 Fission
Learning Objectives
- Describe the process of nuclear fission in terms of its product and reactants
- Calculate the energies of particles produced by a fission reaction
- Explain the fission concept in the context of fission bombs and nuclear reactions
Nuclear Reactions

Practice!
| Practice 13.2.1 |
|---|
What is the Q value for this reaction?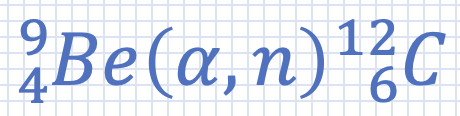 |
| A. 8.4 MeV |
| B. 6.2 MeV |
| C. 7.3 MeV |
| D. 5.7 MeV |
| E. 3.5 MeV |

Discuss!
When the isotope 27Al is irradiated with alpha particles, the products from each aluminum nucleus are a neutron and a nuclide that emits positrons to give the stable isotope 30Si.
Write nuclear equations for these two processes.
Fission

Practice!
| Practice 13.2.2 |
|---|
Find the unknown atomic number and mass number respectively, for the following reaction: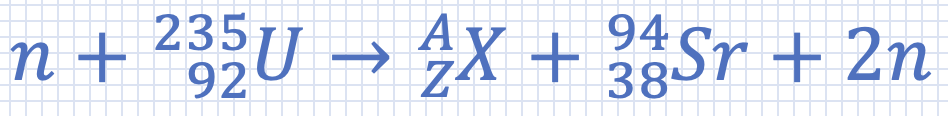 |
| A. 141, 53 |
| B. 140, 54 |
| C. 53, 41 |
| D. 54, 140 |
| E. 54, 141 |
| Practice 13.2.3 |
|---|
Approximately how much uranium must undergo fission per day to provide 1000 MW of power? (Assume an efficiency of 30%). The nuclear reaction is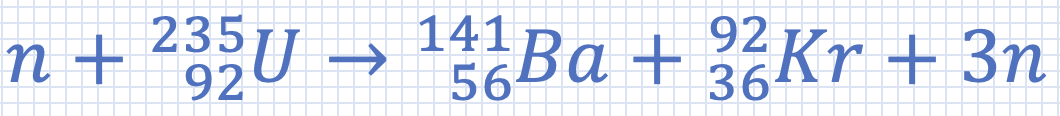 m(n) = 1.008665 u m(U) = 235.043915 u m(Ba) = 140.9139 u m(Kr) = 91.8973 u 1u = 1.66 x 10–27 kg |
| A. 1.0 kg |
| B. 0.35 kg |
| C. 0.23 kg |
| D. 0.46 kg |
| E. 0.1 kg |

Discuss!
The following fission reaction can take place in a nuclear reactor:
n + 235U –> 137Cs + 95Rb + __n
Complete the equation, showing how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
What is the significance of the number of neutrons produced?
Why are the products of the reaction, caesium-137 and rubidium-95, likely to be radioactive?
What type of decay are these isotopes likely to show?
In addition to 235U, fission can also be induced in 239Pu. However, plutonium does not exist naturally. To create plutonium, 238U is bombarded with neutrons. (99.3% of all naturally occurring uranium is 238U, with almost all of the remainder 235U.)
n + 238U –>
Complete the above reaction, clearly showing how 239Pu is formed.
Find Q for the complete reaction.
Fission Reactors
| Practice 13.2.4 |
|---|
| In order to control a nuclear reactor, control rods can be pulled out of or pushed into the reactor core by remote control. These rods control the reactor by |
| A. slowing down the fast neutrons so the neutrons can be absorbed by 238U. |
| B. speeding up slow neutrons so the neutrons can be absorbed by 238U. |
| C. slowing down fast neutrons so they cannot initiate further fusion reactions in 235U. |
| D. speeding up fast neutrons so they cannot initiate further fusion reactions in 235U. |
| E. capturing thermal neutrons so they cannot initiate further fission reactions in 235U. |
| Practice 13.2.5 |
|---|
| A self-sustained chain reaction occurs when the reproduction constant, K, is equal to |
| A. 3.0 |
| B. 2.0 |
| C. 2.5 |
| D. 1.0 |
| E. 0.5 |
| Practice 13.2.6 |
|---|
| When a fast neutron collides with a hydrogen or deuterium nucleus, the most likely result is that |
| A. the neutron has an appreciable gain in kinetic energy, the gain being greatest for head-on collisions. |
| B. the neutron has an appreciable gain in kinetic energy, the gain being greatest for oblique collisions. |
| C. the neutron has an appreciable loss in kinetic energy, the loss being greatest for head-on collisions. |
| D. the neutron has an appreciable loss in kinetic energy, the loss being greatest for oblique collisions. |
| E. the neutron is absorbed by the hydrogen or deuterium nucleus. |
| Practice 13.2.7 |
|---|
| If the moderator were suddenly removed from a nuclear reactor in an electric generating station, what is the most likely consequence? |
| A. No change would occur in the reactor’s operation. |
| B. The nuclear reaction would proceed in the same way, but the reactor would overheat. |
| C. The reactor would become subcritical, and the reaction would die out. |
| D. The reactor would go supercritical, and a runaway reaction would occur. |