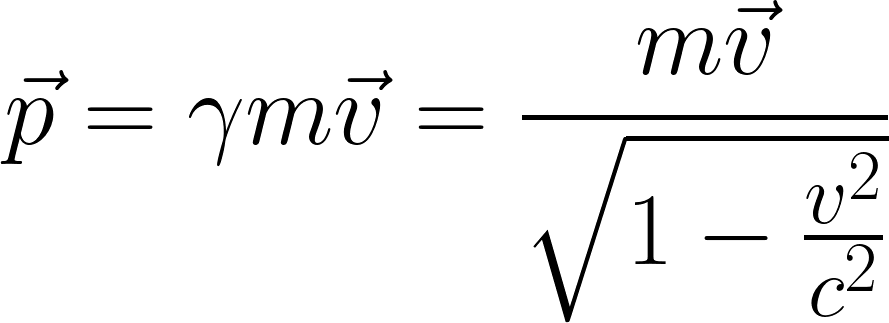Relativistic Momentum

2.2 Relativistic Momentum
Learning Objectives
- Define relativistic momentum in terms of mass and velocity
- Show how relativistic momentum relates to classical momentum
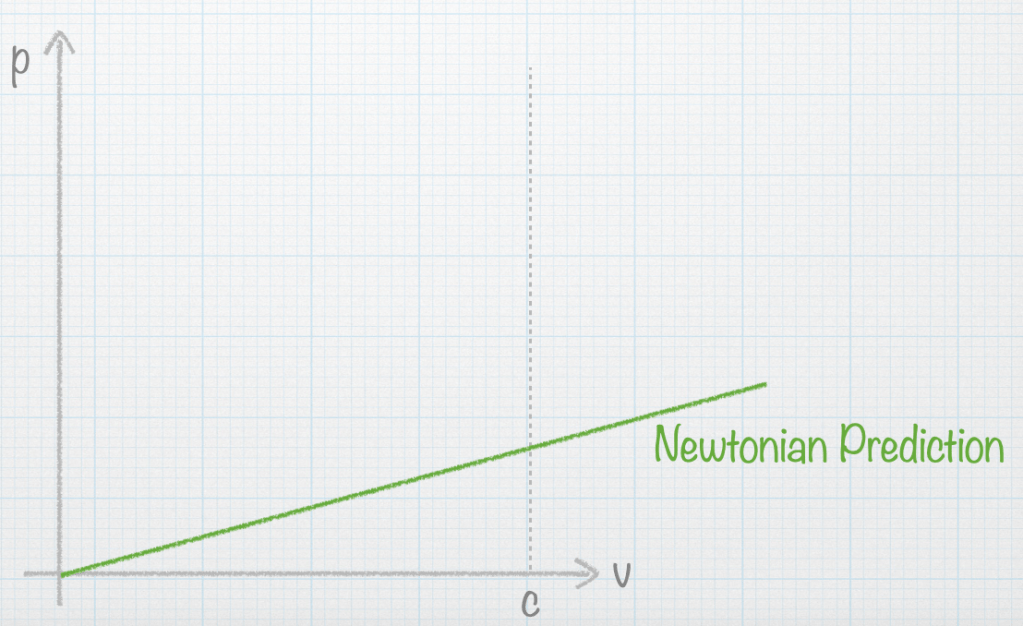
- Show how conservation of relativistic momentum limits objects with mass to speeds less than c
Relativistic momentum 𝐩⃗ is classical momentum multiplied by the relativistic factor γ:

Practice!
| Practice 2.2.1 |
|---|
| Particle A has half the mass and twice the speed of particle B. Is pA less than, greater than, or equal to pB? |
| A. pA < pB |
| B. pA > pB |
| C. pA = pB |
| Practice 2.2.2 |
|---|
| A proton was measured to have momentum 8.00 × 10-20 kg·m/s. What is its speed? |
| A. 0.079c |
| B. 0.157c |
| C. 0.471c |
| D. 0.314c |

Discuss!
As a particle speeds up and approaches c, what happens to the particle’s momentum? Sketch a graph of the particle’s momentum versus its speed.