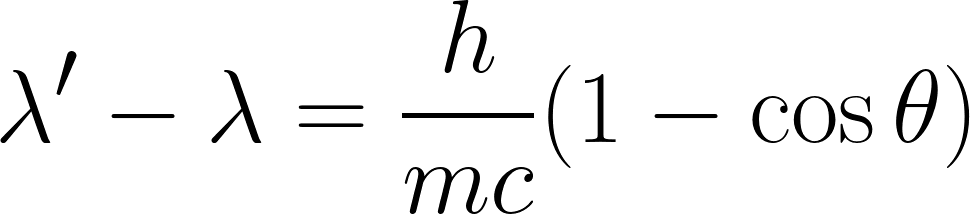The Compton Effect

3.3 The Compton Effect
Learning Objectives
- Describe Compton’s experiment
- Explain the Compton wavelength shift
- Describe how experiments with X-rays confirm the particle nature of radiation
Photons Have Momentum!
Momentum of a photon:
Compton Scattering
Compton Shift

Practice!
| Practice 3.3.1 |
|---|
| When a photon collides with a free electron at rest and the direction of motion of the photon changes, … |
| A. the magnitude of the momentum of the photon does not change. |
| B. the momentum of the electron does not change. |
| C. the kinetic energy of the electron does not change. |
| D. the total energy of the photon does not change. |
| E. both the magnitude of the momentum and the total energy of the photon decrease. |
| Practice 3.3.2 |
|---|
| A photon collides with an electron. After the collision the wavelength of the scattered wave is |
| A. greater than or equal to the initial wavelength. |
| B. equal to the initial wavelength. |
| C. less than or equal to the initial wavelength. |
| D. greater than the initial wavelength. |
| E. less or greater depending on the scattering angle. |
| Practice 3.3.3 |
|---|
| A photon whose energy is 8.00 x 10–15 J is scattered off an electron at a 90° angle. What is the wavelength of the scattered wave? |
| A. 2.73 x 10–11 m |
| B. 2.25 x 10–11 m |
| C. 2.50 x 10–11 m |
| D. 2.40 x 10–12 m |
| E. 2.48 x 10–11 m |