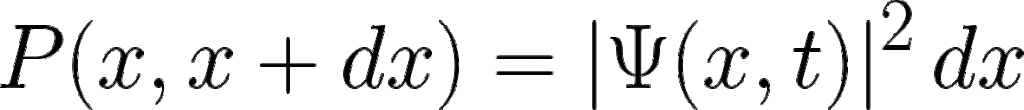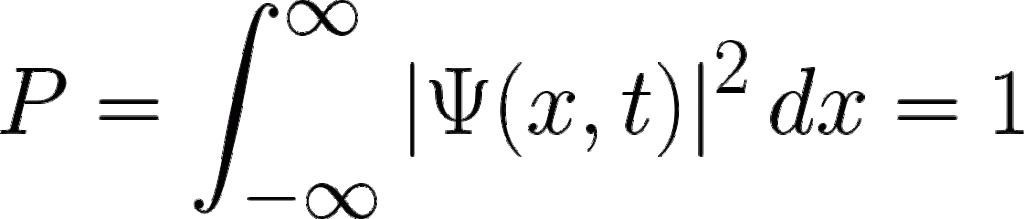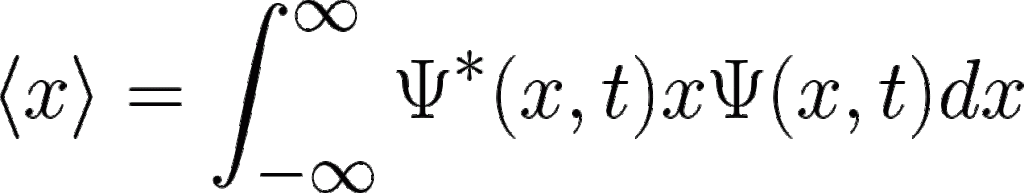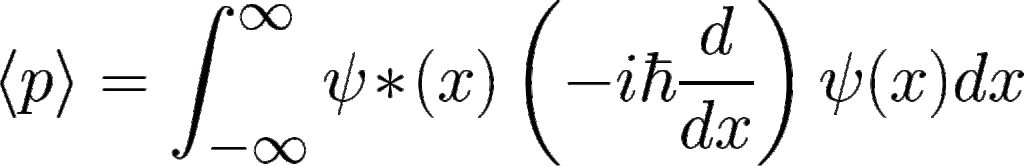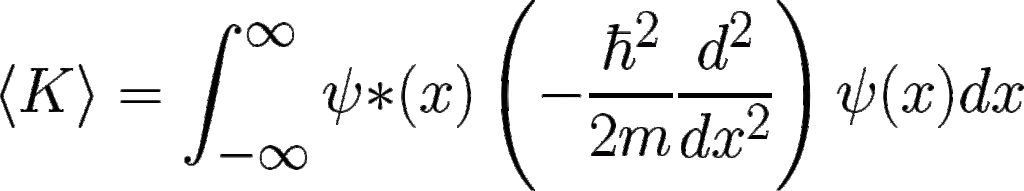Wave Functions

5.1 Wave Functions
Learning Objectives
- Describe the statistical interpretation of the wave function
- Use the wave function to determine probabilities
- Calculate expectation values of position, momentum, and kinetic energy
Probability Density
Probability to find a particle in a small interval (x, x + dx)

Practice!
| Practice 5.1.1 |
|---|
Which of the following hypothetical wave functions for a particle in some realistic potential U(x) is acceptable? |
| A. (a) |
| B. (b) |
| C. (c) |
| D. more than one |
| E. none of them |
| Practice 5.1.2 |
|---|
Which of the following wavefunctions corresponds to a particle more likely to be found on the left side? |
| A. (a) |
| B. (b) |
| C. (c) |
| D. more than one |
| E. none of them |
Normalizing the Wave Function
Normalization Condition

Discuss!
What is A when the wave function 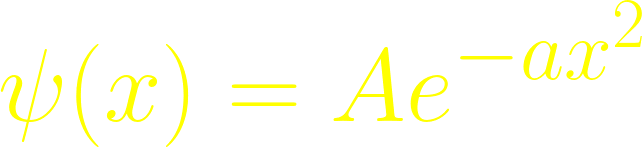 is normalized?
is normalized?

Complex Conjugate

Discuss!
If 𝑎 = 3 + 4𝑖, what is the product 𝑎∗𝑎?
Suppose that a particle with energy E is moving along the x-axis and is confined in the region between 0 and L. One possible wave function is
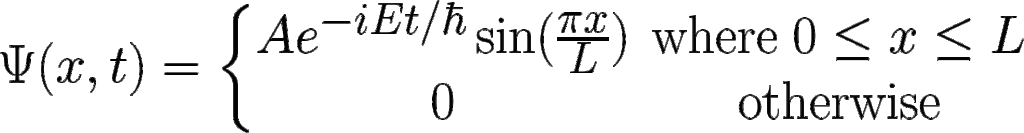
Determine the normalization constant.
Expectation Value
Expectation Value of Position
Expectation Value of Momentum
Expectation Value of Kinetic Energy