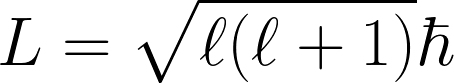The Hydrogen Atom

7.1 The Hydrogen Atom
Learning Objectives
- Describe the hydrogen atom in terms of wave function, probability density, total energy, and orbital angular momentum
- Identify the physical significance of each of the quantum numbers (n, l, ml) of the hydrogen atom
- Distinguish between the Bohr and Schrödinger models of the atom
- Use quantum numbers to calculate important information about the hydrogen atom
Quantum Particles in 3-d Potentials

Practice!
| Practice 7.1.1 |
|---|
| Consider a particle in a two-dimensional (infinite) well, with Lx = Ly. Compare the energies of the (2,2), (1,3), and (3,1) states. |
| A. E(2,2) > E(1,3) = E(3,1) |
| B. E(2,2) = E(1,3) = E(3,1) |
| C. E(1,3) = E(3,1) > E(2,2) |
| Practice 7.1.2 |
|---|
| Consider a particle in a two-dimensional (infinite) well. If we squeeze the box in the x-direction (i.e., Lx < Ly) compare E(1,3) with E(3,1): |
| A. E(1,3) < E(3,1) |
| B. E(1,3) = E(3,1) |
| C. E(1,3) > E(3,1) |
Energies for a particle in a 3-d box (equal sides of length a)

Discuss!
Draw an energy level diagram for a particle in a 3-d box with equal sides of length a.
(a) Show the energies and label (nx,ny,nz) for the first 11 states of the particle in the 3D box, and write the degeneracy D for each allowed energy.
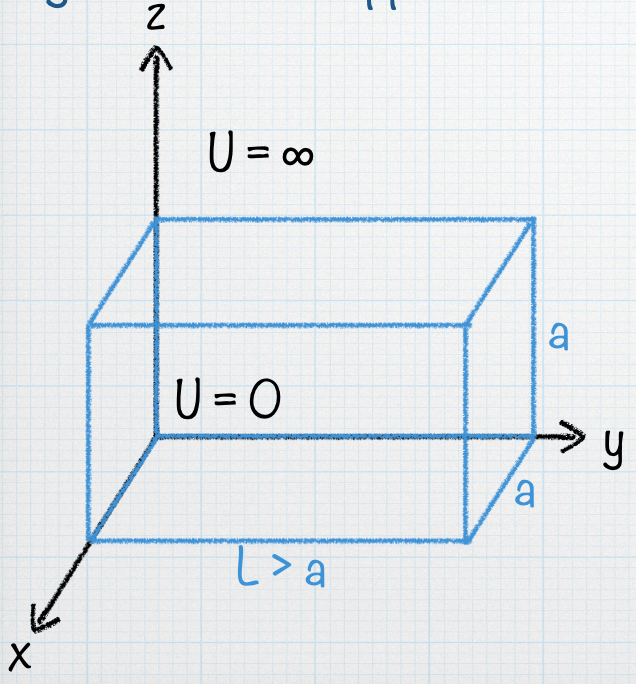
(b) Assume that the box is stretched only along the y-direction. What do you think will happen to the cube’s energy levels?
The Hydrogen Atom
Quantized Energy
n = 1, 2, 3, …
Quantized Angular Momentum
ℓ = 0, 1, 2, …, n-1
Space Quantization of Angular Momentum
mℓ = -ℓ, …, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, …, +ℓ
Quantum States of the Hydrogen Atom


Practice!
| Practice 7.1.3 |
|---|
| When the principal quantum number is n = 5, how many different values of ℓ are possible? |
| A. 0 |
| B. 1 |
| C. 2 |
| D. 3 |
| E. 5 |
| F. 6 |
| G. 9 |
| Practice 7.1.4 |
|---|
| When the principal quantum number is n = 5. how many different values of mℓ are possible? |
| A. 0 |
| B. 1 |
| C. 2 |
| D. 3 |
| E. 5 |
| F. 6 |
| G. 9 |
| Practice 7.1.5 |
|---|
| What angle does the orbital angular momentum make with the z axis of a hydrogen atom in the state n = 3, ℓ = 2, mℓ = –1? |
| A. -66° |
| B. 66° |
| C. 24° |
| D. 114° |
| E. 73° |
| Practice 7.1.6 |
|---|
| A hydrogen atom in the 4f state has a total orbital angular momentum of |
| A. 2√3 ħ |
| B. 3 ħ |
| C. 6 ħ |
| D. √3 ħ |
| E. 12 ħ |

Discuss!
For hydrogen in a 4f state:
(a) Find all the possible values of Lz
(b) Find all the possible values of θ