Medical Physics Course Learning Objectives
and why they matter.
This introductory course in medical physics provides a comprehensive foundation in the principles and applications of radiation in medicine. Students will explore fundamental concepts of atomic and nuclear physics, radiation interactions with matter, and the production and detection of various types of radiation. The course covers essential topics in radiation oncology and therapy, including the operation of linear accelerators, dosimetry, and radiation safety protocols. Students will also gain insights into medical imaging technologies and emerging trends in the field. By the end of the course, students will have developed a solid understanding of how physics principles are applied in medical settings to diagnose and treat patients, while emphasizing the importance of radiation protection and quality assurance in healthcare environments.
Upon completion of this course students will:

1. Classify different types of radiation and explain their interactions with matter, demonstrating proficiency in using common radiation detection and measurement instruments.
Why it’s important: Understanding radiation types and interactions is fundamental to safely working with radiation in medical settings and accurately measuring radiation for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.

2. Calculate and interpret radiation quantities including exposure, absorbed dose, and dose equivalent, explaining their implications in medical contexts.
Why it’s important: Accurate quantification of radiation is crucial for patient safety, treatment planning, and assessing potential health risks in medical procedures.
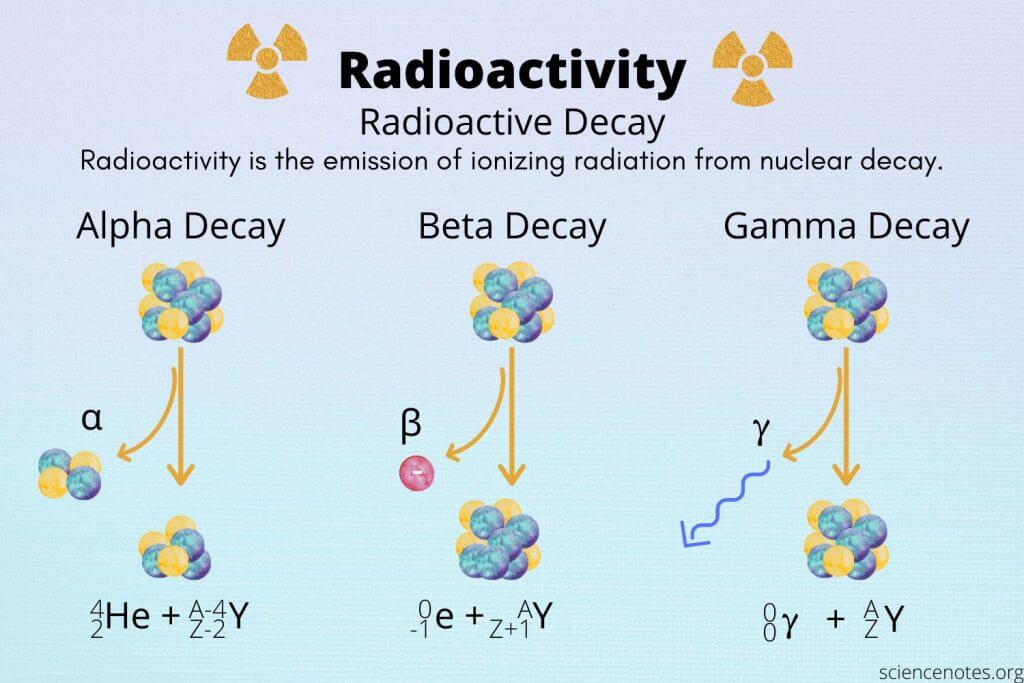
3. Describe radioactive decay processes and analyze decay modes (alpha, beta, gamma), illustrating their significance in medical and environmental applications.
Why it’s important: Knowledge of decay processes is essential for using radioisotopes in medical imaging and therapy, as well as understanding radiation safety in healthcare and environmental settings.

4. Compare how photons and charged particles interact with biological tissue, examining energy deposition mechanisms and resulting biological effects.
Why it’s important: This understanding is critical for predicting treatment outcomes in radiation therapy and assessing potential risks of radiation exposure to patients and medical staff.
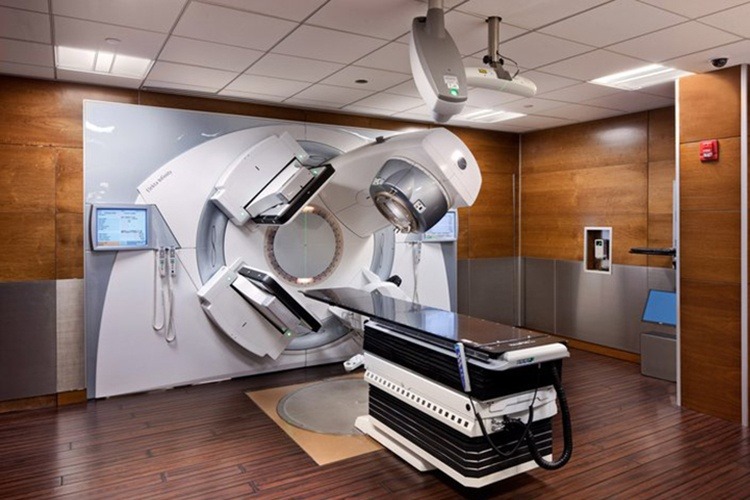
5. Explain the components and operational principles of linear accelerators used in radiation therapy, including magnetrons and beam modifiers.
Why it’s important: Familiarity with these devices is essential for those working in radiation oncology, ensuring proper operation, maintenance, and quality assurance of treatment equipment.

6. Apply radiation safety protocols in medical environments, including performing shielding calculations, adhering to dose limits, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Why it’s important: Implementing proper safety measures protects patients, medical staff, and the public from unnecessary radiation exposure, which is a core responsibility in medical physics.

7. Perform radiation dosimetry, apply appropriate correction factors, and implement quality assurance measures to ensure accurate radiation delivery in therapeutic settings.
Why it’s important: Precise dosimetry and quality assurance are critical for effective treatment outcomes and patient safety in radiation therapy.

8. Illustrate the mechanisms and technologies used to produce photons and particulate radiation for medical applications, with emphasis on x-ray tubes and particle accelerators.
Why it’s important: Understanding radiation production is crucial for optimizing imaging and treatment techniques, troubleshooting equipment issues, and developing new medical physics applications.
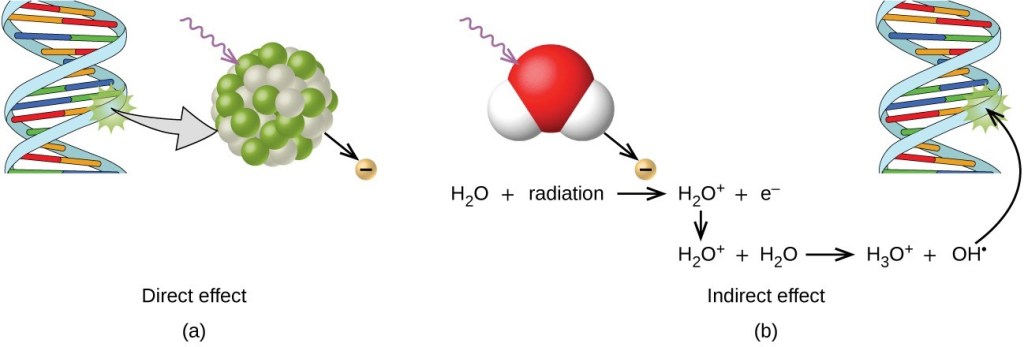
9. Discuss the acute and chronic biological effects of radiation exposure on tissues, cells, and organs, relating these effects to radiation protection practices.
Why it’s important: This knowledge is essential for making informed decisions about the risks and benefits of radiation-based medical procedures and for developing effective radiation protection strategies.
10. Evaluate emerging technologies in radiation detection, therapy techniques, and medical imaging, explaining how these advancements can improve patient care and treatment outcomes.
Why it’s important: Staying informed about technological advancements is crucial for continual improvement in medical physics practices, leading to better diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficacy.