Photon Interactions with Matter

Recommended Reading
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the total attenuation coefficient and its significance in the attenuation of X-rays and gamma rays.
- Explain the mechanisms of coherent scattering, photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, pair production, and photodisintegration.
- Understand and calculate the likelihood of different attenuation modes occurring based on photon energy and material properties.
Total Attenuation Coefficient
Photoelectric Effect
Questions about the photoelectric effect:
- Describe what happens to the energy of a photon that undergoes a photoelectric interaction.
- Describe the characteristics of a material that affect the probability of photoelectric interactions.
- Describe the relationship between the probability of photoelectric interactions and photon energy.
- Sketch a K-edge and explain what determines its energy.
Compton Scattering
Questions about the Compton effect:
- Describe what happens to the energy of a photon in a Compton interaction.
- Describe the characteristics of a material that affect the probability of Compton interactions.
- Discuss the factors that determine the amount of energy lost by photons in a Compton interaction.
- Discuss what determines the angle of scatter in a Compton interaction.
Pair Production

Practice!
| Practice 7.1.1 |
|---|
Which of the following energy diagrams correctly describes the photoelectric effect?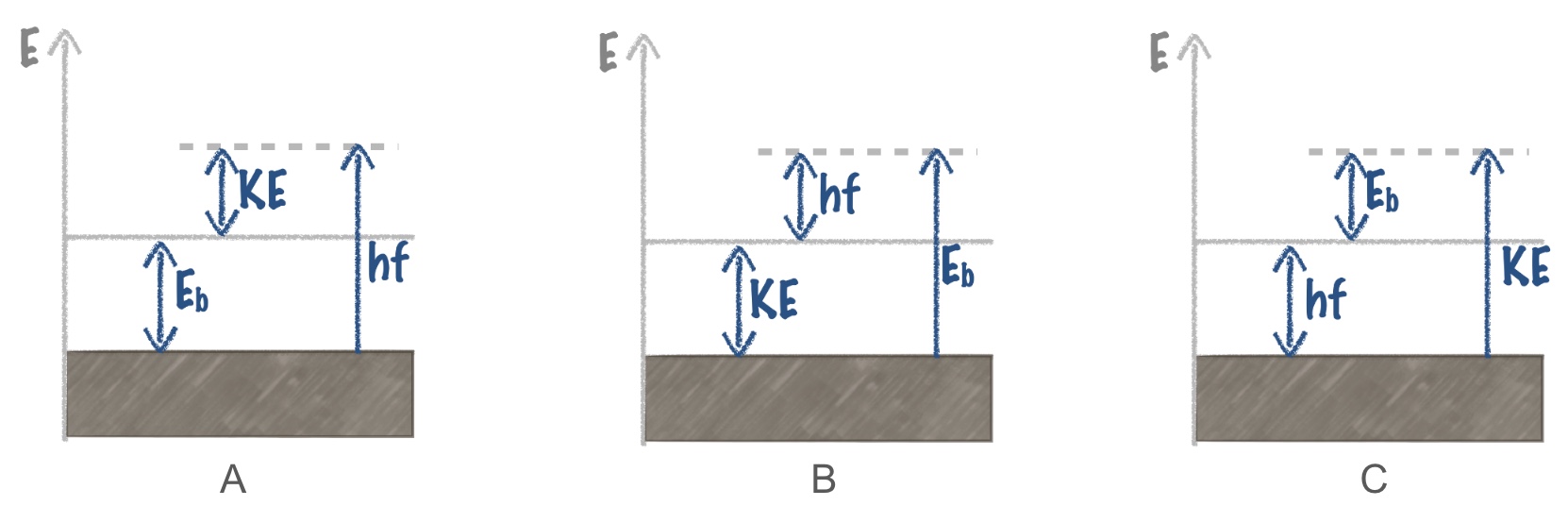 |
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. None of the above |
| Practice 7.1.2 |
|---|
| When a photon collides with a free electron at rest and the direction of motion of the photon changes, … |
| A. the magnitude of the momentum of the photon does not change. |
| B. the momentum of the electron does not change. |
| C. the kinetic energy of the electron does not change. |
| D. the total energy of the photon does not change. |
| E. both the magnitude of the momentum and the total energy of the photon decrease. |
| Practice 7.1.3 |
|---|
| A photon collides with an electron. After the collision the wavelength of the scattered wave is |
| A. greater than or equal to the initial wavelength. |
| B. equal to the initial wavelength. |
| C. less than or equal to the initial wavelength. |
| D. greater than the initial wavelength. |
| E. less or greater depending on the scattering angle. |
| Practice 7.1.4 |
|---|
| A photon whose energy is 8.00 x 10–15 J is scattered off an electron at a 90° angle. What is the wavelength of the scattered wave? |
| A. 2.73 x 10–11 m |
| B. 2.25 x 10–11 m |
| C. 2.50 x 10–11 m |
| D. 2.40 x 10–12 m |
| E. 2.48 x 10–11 m |

Discuss!
Photons with wavelength = 250 nm hit a metal surface and emit photoelectrons with a maximum kinetic energy of 1.0 eV. What is the electron minimum binding energy in the metal?
A photon with energy 8.00 x 10–15 J is scattered off an electron at a 90° angle. What is the wavelength of the scattered photon?
X rays are produced in a tube operating at 24.0 kV. This produces x-ray photons with a maximum energy of 24.0 keV (something we will discuss in detail later in the semester). After emerging from the tube, the x rays strike a target and undergo Compton scattering through an angle of 45°.
a) What is the kinetic energy of the electrons after the collision?
b) What is the original (incident) x-ray wavelength?
c) What is the wavelength of the scattered x rays?
d) What is the energy of the scattered x rays?